Our Product
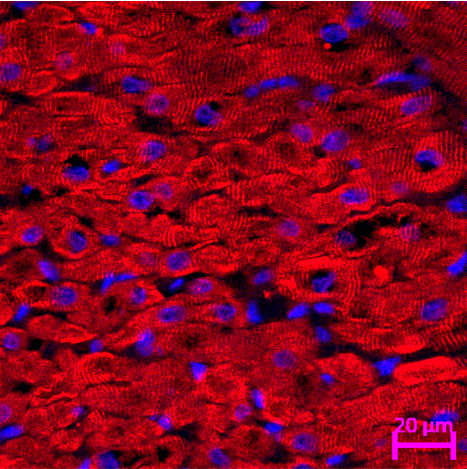
Heart Engineering
Myocardial infarction (heart attack) is damage to the heart muscle due to blockage of the coronary arteries that supply the area. Mild to moderate heart muscle damage can be reduced by using percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), namely installing a ring or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) or what is usually called a bypass.
However, heart muscle that has been damaged cannot heal on its own, and large and severe areas of infarction can cause heart failure. Until now, the procedure to treat heart failure is a heart transplant from a donor or an iron heart/ventricular assist device (VAD), which takes a lot of time and money, and the chance of a suitable heart is only 4.7% (Hsich, 2016). Therefore, the need to look for alternatives to transplantation and VAD to treat heart failure is very necessary.
Our therapy focuses on regeneration methods by repairing damaged heart walls with biological matrix and cell therapy so that it can stimulate the growth of heart muscle tissue back to normal. The aim of this method is to restore heart function and improve the patient’s quality of life after a heart attack or myocardial infarction.
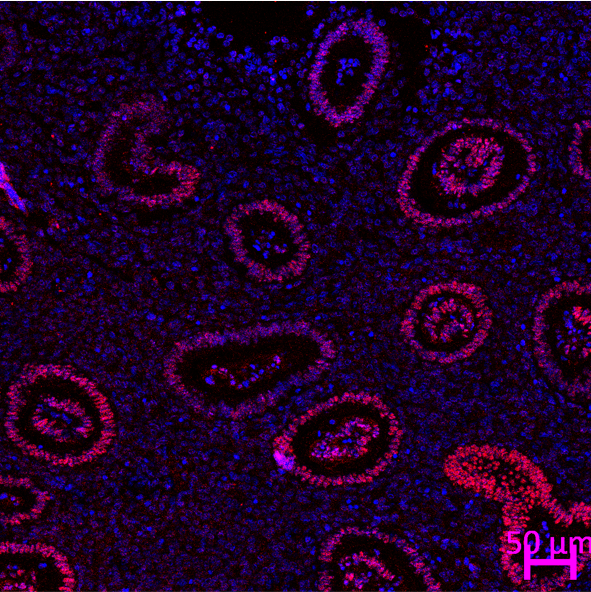
Womb Engineering
Pregnancy failure can be caused by 1/3 embryo factors and 2/3 uterine factors (Simón et al., 1998). Uterine factors are caused by hormonal disorders, infections, or surgical trauma.
Until now, the existing therapy to grow a thin uterine wall is hormonal therapy, or plasma therapy. However, in certain patients, this does not provide an improvement response.
Our team developed therapy for uterine walls that are not responsive to existing treatment, with the principle of regeneration to regrow the uterine wall using biological womb patches and cell therapy, using a uterine catheter (UteroFIX®) so that it makes maximum contact with the uterine wall being treated.
UteroFIX® is a uterine catheter specifically designed to suit the anatomical size of Asian women so that it does not cause mules or rejection, aimed at applying medication to the uterine wall, preventing adhesions in the uterine wall and stopping bleeding.


Artificial Skin
Until now, in situations where skin is needed to cover missing skin, it is by taking the patient’s own healthy skin. However, this is very limited if the patient does not have enough healthy skin, or is seriously ill.
Meanwhile, the availability of artificial skin to replace damaged or lost skin, such as in cases of burns, accidents or malignant conditions, is very limited.
This makes it a challenge for clinicians to treat all patients who need skin replacement. Especially in cases of severe burns with a large burn area (>40%).
Our artificial leather products are engineered to mimic the natural structure and function of human skin. This innovation is designed for a variety of medical applications to close open skin such as tissue grafts.
